What is the Difference Between ECU, MCU and MPU?
Introduction
ECU (Engine Control Unit) and MCU (Microcontroller Unit) are two components that play an important role in automotive electronic systems. Although they are both processors used in control systems, there are some significant differences in their design, functionality, and applications.
What is ECU (engine control unit)?
ECU is an electronic device specially used to control engine operation. It ensures efficient engine operation by monitoring and regulating various engine parameters. ECU usually consists of one or more microprocessors and a series of sensors to monitor the working status of the engine in real-time and make corresponding adjustments according to different conditions.
The main functions of the ECU include ignition control, fuel injection control, cylinder pressure monitoring, emission control, etc. It receives input signals from various sensors (such as oxygen sensor, temperature sensor, air flow sensor, etc.) and outputs appropriate control signals by controlling actuators (such as fuel injectors, throttle valves, etc.). In this way, the ECU can ensure the engine provides optimal performance and fuel economy under different operating conditions.
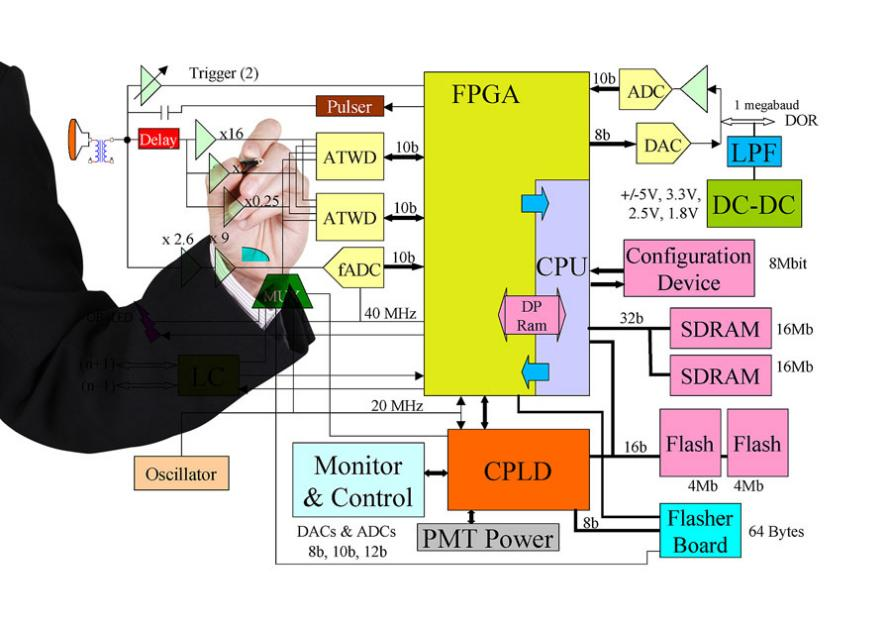
Figure1-ecu principle
What is an MCU (Microcontroller Unit)?
MCU is a single-chip microcomputer that integrates a processor, memory, and various peripherals. It is usually used to control various aspects of electronic equipment or systems, such as home appliances, industrial automation, consumer electronics and other fields. Compared with ECU, MCU has a wider range of applications.
At the heart of an MCU is a microprocessor, whose speed and performance depend on specific product needs. It also includes memory (such as flash memory, RAM), input and output interfaces (such as serial port, parallel port, analog input, etc.) and other specific peripherals signals based on preset logic and algorithms to achieve the required functions.
Figure2-Microcontroller Unit
MPU vs MCU
MPU is a chip that only contains the processor core, unlike MCU which integrates memory and peripherals. MPU is widely used in high-performance computers, servers, embedded systems, and other fields. It can perform complex calculations and tasks and often has greater processing power and memory capacity.
Compared with MPU, MCU is more portable, has low power consumption, and has lower cost. It is suitable for application scenarios that do not require high performance, such as embedded devices, electronic toys, sensor controls, etc. The advantage of MCU is that it is highly integrated, easy to use and program, and can implement more complex functions.
As key components in automotive electronic systems, ECUs, and MCUs are used for engine control and general control respectively. ECU focuses on engine operating condition monitoring and adjustment, while MCU is widely used for control needs in various fields. Furthermore, an MPU is a chip that contains only a processor core and is used in high-performance computing and embedded applications.

Figure3-MPU is widely used in high-performance computers
3. ECU VS MCU
Before moving on to discuss the differences between ECU (Engine Control Unit) and MCU (Microcontroller Unit), it is worth noting that their design and functionality vary depending on the application. Here are some of their main differences:
- Application fields: ECU is mainly used in the automotive industry, especially engine control, such as ignition systems, fuel injection, and emission control. MCUs are widely used in various industries, including home appliances, consumer electronics, industrial automation, etc., to control and manage multiple equipment and systems.
2. Processing capacity: Since the ECU is mainly used for engine control, its processing capacity is usually high. The ECU needs to monitor and respond to engine parameter changes in real time and make corresponding adjustments, so it requires fast and efficient processing capabilities. MCUs usually have lower processing capabilities and are suitable for simpler control tasks.

Figure4-MCU
- Integration: ECUs often contain multiple microprocessors and specialized chips to meet the monitoring and control needs of all aspects of the engine. These components can be connected via a bus for data exchange and collaboration. In contrast, an MCU is typically a single-chip solution that integrates a processor, memory, and various peripherals to provide a more streamlined design and integration.
- Specificity: ECUs are designed to meet the specific needs of engine control, so they usually have specialized hardware and software functions. These functions include fault diagnosis, adaptive adjustment, closed-loop feedback control, etc. In comparison, MCU design is more versatile and can be customized according to different application requirements.
- Power consumption and reliability: Since ECUs usually need to run for a long time and work in high temperatures and harsh environments, they have higher requirements for power consumption and reliability. ECUs need to maintain stable performance and ensure system reliability and durability. MCUs generally have lower power consumption and can operate in various environmental conditions.
Although ECUs and MCUs are both processors used to control systems, they differ in application fields, processing capabilities, integration, specificity, power consumption, and reliability. For the automotive industry, ECU is the core of engine control, while MCU is used to implement various other control needs. For other industries, MCU is a versatile and flexible control solution.
 What is the Difference Between ECU, MCU and MPU?10/27/2023 658
What is the Difference Between ECU, MCU and MPU?10/27/2023 658ECU (Engine Control Unit) and MCU (Microcontroller Unit) are two components that play an important role in automotive electronic systems. Although they are both processors used in control systems, there are some significant differences in their design, functionality, and applications.
Read More >


